How To Properly Store Sealed Chromatography Vials
Proper storage of sealed chromatography vials is a critical yet often overlooked component of laboratory processes. Correctly storing vials impacts sample integrity, prevents contamination, and encourages accurate experimental results. Use this guide to learn about properly storing sealed chromatography vials, including best practices for handling and organization to protect your samples and optimize laboratory operations.
What Are Chromatography Vials?
Chromatography vials are essential containers used to hold samples for analysis. These vials vary in material, size, and design to accommodate a wide range of applications. Glass vials are commonly used for their chemical resistance and ability to prevent leaching, while plastic vials are lighter and often used for less sensitive samples. Sealed vials typically include caps and septa, which are barriers to contamination and sample evaporation. Choosing the right vial is the first step in ensuring proper storage and successful experimental outcomes.
Preparing Vials for Storage
Vials must be clean, dry, and free of contaminants before using them for storage. Thoroughly rinse the vials with an appropriate solvent to eliminate residual chemicals or particulates from previous use. Sterilize the vials, particularly for sensitive or biological samples, to avoid microbial contamination.
Proper sealing techniques are also critical; ensure the vial caps are securely in place to prevent leaks or exposure to environmental factors. Taking these preparatory steps reduces the risk of compromising your samples during storage.
Material Compatibility and Considerations
The materials used in chromatography vials play a pivotal role in storage requirements and sample compatibility. Glass vials are generally preferred for organic solvents due to their inert nature, while plastic vials are better for aqueous solutions. However, certain samples may interact chemically with these materials, leading to contamination or degradation.
For example, acidic samples might react with the surface of glass vials over time. Check that the vial material is compatible with your sample’s composition to mitigate potential chemical interactions and preserve sample integrity.
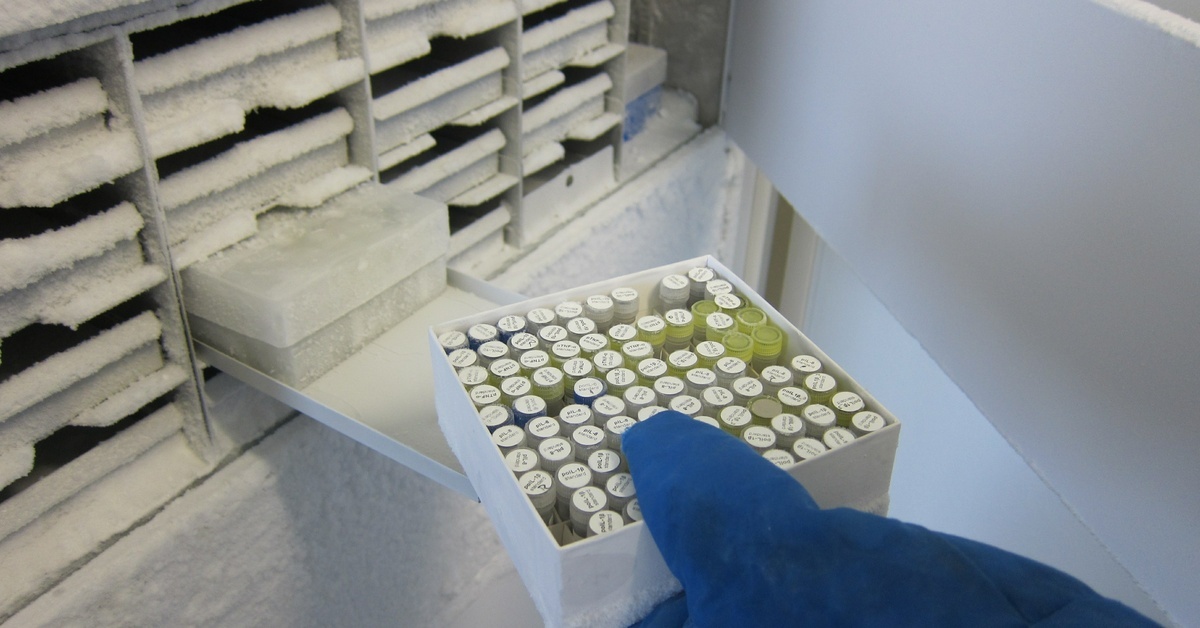

Recommended Temperature Settings
Maintaining the correct temperature for your sealed chromatography vials is crucial to prevent degradation and maintain sample stability. Most organic and biological samples in chromatography require refrigeration, typically above 32 degrees Fahrenheit, to maintain their chemical properties. Some highly sensitive samples, such as certain enzymes, may demand storage in ultra-low freezers at temperatures as low as -112 degrees for long-term storage.
Conversely, volatile compounds may evaporate or degrade if stored at warmer temperatures above 70 degrees. Always refer to your samples’ chemical or biological requirements to set the ideal storage temperature and minimize risks.
Humidity Control in Storage Areas
Excess humidity risks the integrity of stored samples by introducing moisture, leading to hydrolysis and degradation. A low-humidity or moisture-free environment is vital, particularly for hygroscopic samples or those housed in plastic vials. Storage options such as desiccators, which remove moisture from the air, or temperature-controlled chambers with built-in humidity control are invaluable. Regularly monitor the storage area’s humidity levels using hygrometers to ensure they remain within acceptable ranges.
Avoiding Light Exposure
Light-sensitive samples rapidly degrade if exposed to UV rays or intense lighting, rendering them unusable for analysis. To combat this, consider using amber vials or opaque storage containers that block light while protecting the sample’s integrity.
Additionally, store vials in dark, enclosed spaces like cabinets or specialized fridges designed for light-sensitive materials. Even in labs with controlled lighting, extra precautions such as wrapping vials in foil protect highly sensitive materials.
Storage Orientation and Positioning
Positioning your vials during storage makes a difference in safeguarding your samples. Storing vials upright is recommended in most cases, as it minimizes the risk of leaks and prevents seals from coming into prolonged contact with liquid contents.
For long-term storage, consider using vial racks or compartments that keep the vials secure and organized. Horizontal storage or overcrowding may lead to spillage or physical damage, complicating lab operations and risking contamination.
Labeling for Easy Identification
Effective labeling is essential for managing your vial inventory and retrieving the correct sample. Use waterproof, chemical-resistant labels for readability over time, including key details such as the sample name, concentration, date of preparation, and expiration date. Use color-coded labels or barcodes connected to a digital inventory system for further organization. Proper labeling saves valuable lab time and reduces the likelihood of mix-ups and errors in analysis.

Storage Organization Best Practices
A structured storage system is key to maintaining a functional and efficient laboratory. Group your vials by sample type, sensitivity, or analytical priority to facilitate easy access and retrieval. Use clearly labeled shelves, compartments, and racks designed for vial storage to keep the area uncluttered. A digital inventory tracking system further enhances your lab management capabilities, allowing you to monitor quantities and conditions at a glance.
Preventing Chemical Degradation Over Time
Even with optimal storage conditions, some samples are prone to chemical degradation over extended periods. Monitor your vials regularly for signs of discoloration, precipitation, or odor changes to mitigate this. Follow recommended guidelines specific to each sample type, rotating stored vials based on expiration dates. Proper maintenance and timely use of samples contribute to accurate, reproducible experimental results.
Using Specialized Storage Equipment
Investing in specialized storage equipment offers unparalleled protection and convenience for your samples. High-quality refrigeration units with temperature and humidity controls and vacuum-sealed desiccators provide an optimal environment for sensitive materials.
For large-scale operations, temperature-controlled chambers provide precise regulation for storing larger quantities of vials. These investments are invaluable for safeguarding high-value samples and maintaining operational efficiency.
Regular Maintenance of Stored Vials
Schedule regular checks so seals remain intact and samples show no signs of degradation or contamination. Replace damaged vials or overaged samples to avoid cross contamination. Staying proactive with storage protocols ensures the ongoing reliability of your stored materials and safeguards your lab’s productivity.
Proper storage of sealed chromatography vials enables success in lab experiments and research. From choosing the right vial materials to maintaining the ideal storage environment, each step in your storage process impacts the integrity and reliability of your samples.
Equip your lab with high-quality storage solutions from Ibis Scientific to stay consistent in your maintenance routine and leverage labeling and organization systems to streamline operations. Follow these best practices to focus less on troubleshooting and more on delivering accurate, groundbreaking results.
Recent Posts
-
The Role of Desiccants in Protecting Hygroscopic Chemicals
Hygroscopic chemicals readily absorb moisture from the surrounding environment, leading to compromis …May 19th 2025 -
All About Pairing Containers With Corrosive Substances
Handling corrosive substances is critical in many industries, including manufacturing, pharmaceutica …May 12th 2025 -
Why Solvent Purity Is Crucial in the World of Chemistry
When producing accurate and reliable results in chemistry, solvent purity is non-negotiable. Many se …May 11th 2025